ID2 differentially influences LTi-like cells in different tissues
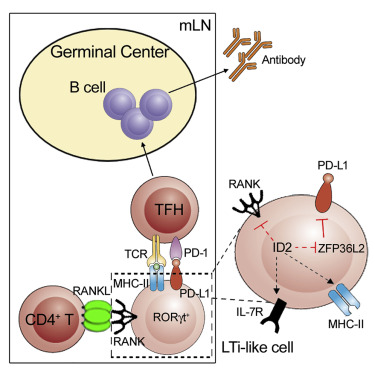
CD4+ T cell-derived RANKL is crucial for maintenance of LTi-like cells in the mLN
The mLN LTi-like cells restrain Tfh through ID2- and PD-L1-dependent pathways
ID2 promotes PD-L1 expression in the mLN LTi-like cells by translational regulation
Lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi)/LTi-like cells are critical for lymphoid organogenesis and regulation of adaptive immunity in various tissues. However, the maintenance and regulation mechanisms of LTi-like cells among different tissues are not clear yet. Here, we find that LTi-like cells from different tissues display heterogeneity. The maintenance of LTi-like cells in the mesenteric lymph node (mLN), but not the gut, requires RANKL signaling from CD4+ T cells. LTi-like cells from the mLN, but not the gut, could in turn inhibit the development of T follicular helper cells and subsequent humoral responses during intestinal immunization in an ID2- and PD-L1-dependent manner. Together, our findings implicate that the interaction between LTi-like cells and T cells in the mLN could precisely control the intestinal mucosal adaptive immune response.
Link:https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(20)30917-7

Copyright © 2017 Institute for Immunology Tsinghua University
Contact Address: Room D302, Medical Science Building, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Tel: (86) 10-62776420 Fax: (86) 10-62776420
