Transcription factor Ascl2 promotes germinal center B cell responses by directly regulating AID transcription
Lin Sun,1,2 Xiaohong Zhao,1 Xindong Liu,3 Bo Zhong,4 Hong Tang,5 Wei Jin,1 Hans Clevers,6 Hui Wang,7 Xiaohu Wang,1 and Chen Dong1,8,9,*
1Institute for Immunology and School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
2Tsinghua University-Peking University Joint Center for Life Science, Beijing 100084, China
3Institute of Pathology and Southwest Cancer Center, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China
4State Key Laboratory of Virology, Hubei Key Laboratory of Cell Homeostasis, College of Life Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China 5CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Virology and Immunology, Institute Pasteur of Shanghai, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 6Hubrecht Institute, Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW) and University Medical Centre (UMC) Utrecht, 3584 CT Utrecht, the Netherlands
7Department of Immunology and Center for Inflammation and Cancer, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX 77054, USA
8Beijing Key Lab for Immunological Research on Chronic Diseases, Beijing 100084, China
9Lead contact
*Correspondence: chendong@tsinghua.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109188
Summary
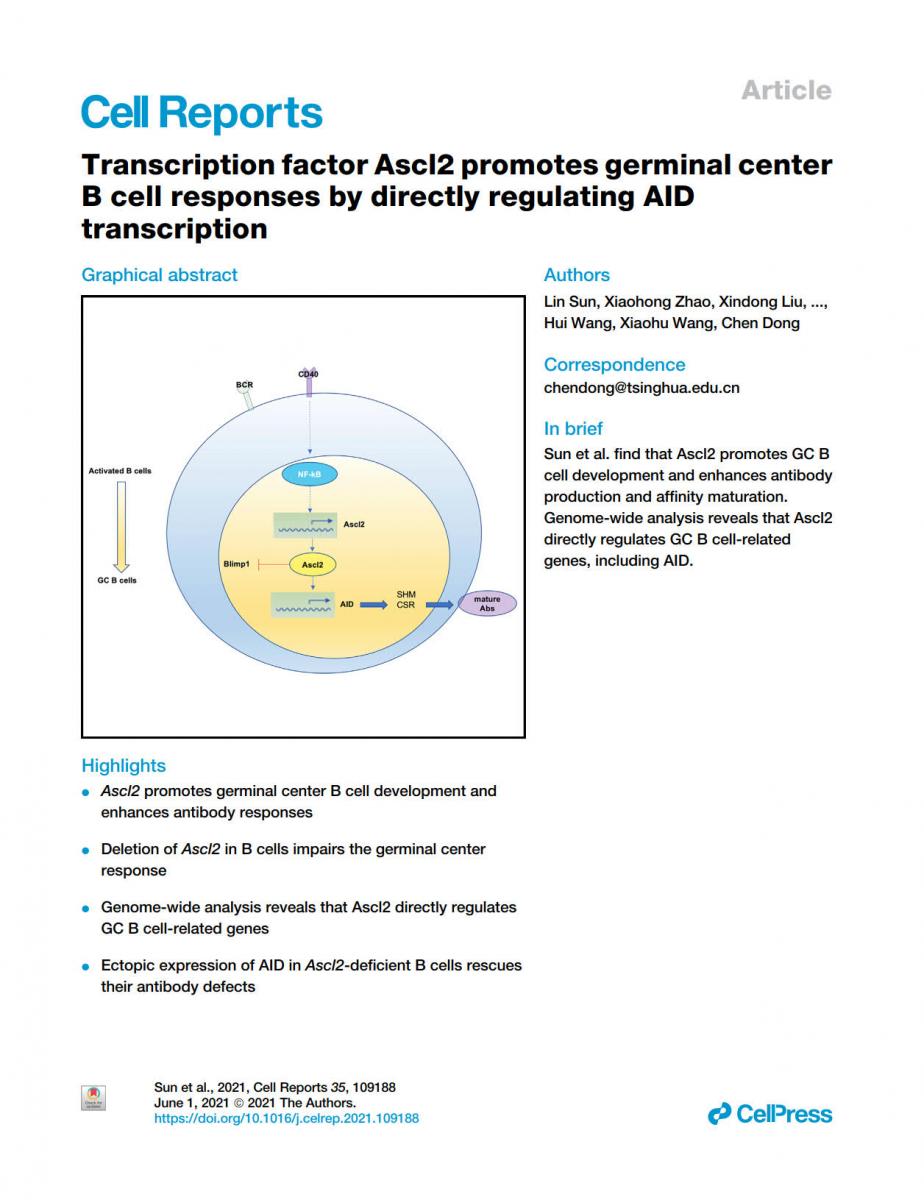
During germinal center (GC) reactions, activated B cells undergo clonal expansion and functional maturation to produce high-affinity antibodies and differentiate into plasma and memory cells, accompanied with class-switching recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is responsible for both CSR and SHM in GC B cells. Transcriptional mechanisms underlying AID regu-lation and GC B cell reactions are still not well understood. Here, we show that expression of Ascl2 transcrip-tion factor is upregulated in GC B cells. Ectopic expression of Ascl2 promotes GC B cell development and enhances antibody production and affinity maturation. Conversely, deletion of Ascl2 in B cells impairs the GC response. Genome-wide analysis reveals that Ascl2 directly regulates GC B cell-related genes, including AID; ectopic expression of AID in Ascl2-deficient B cells rescues their antibody defects. Thus, Ascl2 regulates AID transcription and promotes GC B cell responses.
Link:https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)00534-9

Copyright © 2017 Institute for Immunology Tsinghua University
Contact Address: Room D302, Medical Science Building, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Tel: (86) 10-62776420 Fax: (86) 10-62776420
